Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming many industries, including road safety. Its ability to predict and prevent accidents is significant. AI offers solutions like real-time hazard detection and predictive analytics. Since traffic accidents are a leading cause of injuries and deaths worldwide, AI-driven tools can help reduce risks and improve road safety. This article highlights the roles of AI in accident prediction and prevention, its applications, and the challenges of implementation.
1. Real-Time Hazard Detection
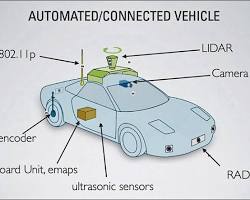
AI enables vehicles and infrastructure to identify and respond to hazards instantly. By using sensors and machine learning, AI systems process data from cameras, radar, and LiDAR. This helps detect dangers like vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, and roadblocks.

AI Applications in Vehicles:
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): AI monitors the road and alerts drivers about hazards. Features include lane departure warnings, blind-spot detection, and collision avoidance.
- Object Recognition: AI recognizes and classifies objects like traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles. This ensures appropriate actions are taken.
Real-time hazard detection reduces reaction time, allowing drivers or systems to act quickly.
2. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics helps anticipate accidents before they happen. AI analyzes large data sets, including traffic patterns, driver behavior, and weather conditions, to predict risky scenarios.
Key Features:
- Driving Pattern Analysis: AI identifies risky habits like speeding or hard braking. These insights can help drivers improve.
- Traffic Flow Prediction: AI predicts congestion and collision zones. This helps drivers and authorities take proactive measures.
Predictive analytics enables better decision-making to reduce accident risks.
3. Collision Avoidance Systems
Collision avoidance systems use AI to monitor surroundings and take automatic actions.
Examples:
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): AI applies brakes autonomously to prevent or reduce collision impacts.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: AI maintains a safe distance by adjusting the vehicle’s speed.
4. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
AI enables seamless communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and road users. This creates a connected ecosystem that enhances safety.

Types of V2X Communication:
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle: Vehicles share speed, location, and direction to avoid collisions.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure: AI processes signals from traffic lights or road sensors to alert drivers about hazards like sharp curves or icy roads.
5. Monitoring Driver Behavior
Driver behavior, such as fatigue or distraction, causes many accidents. AI monitors drivers in real-time to mitigate risks.
Technologies in Use:
- Driver Monitoring Systems: Cameras track facial expressions and eye movements to detect fatigue or distraction.
- Real-Time Alerts: AI warns drivers or suggests breaks if risky behavior is detected.
6. Accident Hotspot Prediction
AI analyzes data to identify accident-prone areas. This helps authorities implement safety measures.
Proactive Measures:
- Improved road signage and lighting
- Installation of speed cameras
- Traffic flow adjustments
7. Road Condition Monitoring
AI monitors road conditions in real-time to identify hazards like potholes or wet surfaces.
Benefits:
- Dynamic Hazard Alerts: Drivers receive warnings about dangerous road conditions.
- Data Sharing: Real-time data helps local authorities address road maintenance issues.
8. Autonomous Driving and Accident Prevention
Autonomous vehicles use AI to navigate safely, reducing human error—the leading cause of accidents.
Capabilities:
- Continuous Learning: AI improves by learning from real-world data.
- Redundant Safety Systems: Multiple layers of safety ensure reliable decision-making.
9. AI in Emergency Response
AI enhances emergency responses after accidents, reducing their impact.
Applications:
- Accident Severity Prediction: AI predicts injury severity, enabling faster medical response.
- Optimized Routing: AI guides emergency vehicles to reach accident sites quickly.
10. Integration with Smart Cities
AI integrates transportation systems with smart city infrastructure for safer urban environments.
Examples:
- Smart Traffic Management: AI optimizes traffic signals to reduce congestion.
- Smart Crosswalks: AI detects pedestrians and alerts vehicles to slow down.
Challenges in AI Implementation
While AI has immense potential, there are challenges to address:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring sensitive data is handled safely
- System Reliability: AI must be fail-safe to avoid malfunctions
- High Costs: Implementation can be expensive for many regions
- Ethical Concerns: Decision-making in critical situations raises ethical issues
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing road safety. From hazard detection to smart city integration, AI tools save lives and reduce accidents. However, challenges like data security and ethical concerns must be resolved for widespread adoption. As technology advances, AI’s role in transforming transportation safety is boundless, paving the way for safer journeys for everyone.
For more interesting articles, please visit our blog: https://techvibezonline.com


